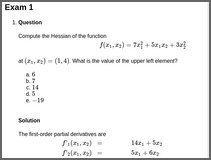
hessian: 2x2 Hessian Matrix (Single-Choice)
hessianCompute the Hessian of the function \[ \begin{aligned} f(x_1, x_2) = 7 x_1^{2} + 5 x_1 x_2 + 3 x_2^{2} \end{aligned} \] at \((x_1, x_2) = (1, 4)\). What is the value of the upper left element?
The first-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f'_1(x_1, x_2) &= 14 x_1 + 5 x_2 \\ f'_2(x_1, x_2) &= 5 x_1 + 6 x_2 \end{aligned} \] and the second-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f''_{11}(x_1, x_2) &= 14\\ f''_{12}(x_1, x_2) &= 5\\ f''_{21}(x_1, x_2) &= 5\\ f''_{22}(x_1, x_2) &= 6 \end{aligned} \]
Therefore the Hessian is \[ \begin{aligned} f''(x_1, x_2) = \left( \begin{array}{rr} 14 & 5 \\ 5 & 6 \end{array} \right) \end{aligned} \] independent of \(x_1\) and \(x_2\). Thus, the upper left element is: \(f''_{11}(1, 4) = 14\).
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
Compute the Hessian of the function \[ \begin{aligned} f(x_1, x_2) = 5 x_1^{2} + 6 x_1 x_2 + 2 x_2^{2} \end{aligned} \] at \((x_1, x_2) = (0, 5)\). What is the value of the lower right element?
The first-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f'_1(x_1, x_2) &= 10 x_1 + 6 x_2 \\ f'_2(x_1, x_2) &= 6 x_1 + 4 x_2 \end{aligned} \] and the second-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f''_{11}(x_1, x_2) &= 10\\ f''_{12}(x_1, x_2) &= 6\\ f''_{21}(x_1, x_2) &= 6\\ f''_{22}(x_1, x_2) &= 4 \end{aligned} \]
Therefore the Hessian is \[ \begin{aligned} f''(x_1, x_2) = \left( \begin{array}{rr} 10 & 6 \\ 6 & 4 \end{array} \right) \end{aligned} \] independent of \(x_1\) and \(x_2\). Thus, the lower right element is: \(f''_{22}(0, 5) = 4\).
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
Compute the Hessian of the function \[ \begin{aligned} f(x_1, x_2) = 2 x_1^{2} -7 x_1 x_2 + 4 x_2^{2} \end{aligned} \] at \((x_1, x_2) = (-2, 3)\). What is the value of the lower right element?
The first-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f'_1(x_1, x_2) &= 4 x_1 -7 x_2 \\ f'_2(x_1, x_2) &= -7 x_1 + 8 x_2 \end{aligned} \] and the second-order partial derivatives are \[ \begin{aligned} f''_{11}(x_1, x_2) &= 4\\ f''_{12}(x_1, x_2) &= -7\\ f''_{21}(x_1, x_2) &= -7\\ f''_{22}(x_1, x_2) &= 8 \end{aligned} \]
Therefore the Hessian is \[ \begin{aligned} f''(x_1, x_2) = \left( \begin{array}{rr} 4 & -7 \\ -7 & 8 \end{array} \right) \end{aligned} \] independent of \(x_1\) and \(x_2\). Thus, the lower right element is: \(f''_{22}(-2, 3) = 8\).
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
num_to_schoice() by providing the other three elements of the Hessian as typical errors. Further random answers are taken from a prespecified range, assuring only integer solutions. Although the Hessian of a quadratic function has only constant elements, an argument vector is given in the exercise because other types of functions might have non-constant Hessians.(Note that the HTML output contains mathematical equations in MathML, rendered by MathJax using ‘mathjax = TRUE’. Instead it is also possible to use ‘converter = “pandoc-mathjax”’ so that LaTeX equations are rendered by MathJax directly.)
Demo code:
library("exams")
set.seed(403)
exams2html("hessian.Rmd", mathjax = TRUE)
set.seed(403)
exams2pdf("hessian.Rmd")
set.seed(403)
exams2html("hessian.Rnw", mathjax = TRUE)
set.seed(403)
exams2pdf("hessian.Rnw")